Measuring principle of oxygen
The oxygen measurement unit is designed to
process signals from a
stabilised zirconium oxide
sensor. Zirconium oxide is a ceramic
material, also characterised as a solid-state electrolyte, that has outstanding
properties as an oxygen-ion conductor at high temperatures.
Within a
certain temperature range, that depends on how the material is doped, such ionic
conductors are able to fill the open spaces in their crystal grating with oxygen
ions. The oxygen ions form on a conductive contact surface, generally of
platinum, and thus the degree of oxygen activity is determined by the
concentration of oxygen in the gas that is measured.In principle, the sensor is
in the form of a solid-state electrolyte that is contacted on both sides, on the
one side by a reference gas such as air and on the other by the gas to be
measured. The sensor is so formed mechanically that the two gases are kept apart
so that there is no possibility of them mixing.Calculation of the oxygen content
(oxygen partial pressure) is carried out based on the measured voltage (emf) by
transforming the following Nernst equation.
Nernst equitation
Calculation is effected in accordance with the equation:
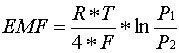
whereby:
EMF = Electromotive force in Volts
R = 8.31J/mol K
T =
Temperature in Kelvin
F = 96493 As/mol
P1 = Oxygen partial pressure on
reference side at 0.20946 bar
P2 = Oxygen partial pressure on the measurement
gas side
With above equation the beside diagram will
result.

